BeagleBone LED software controller. More...
#include <sg_BeagleBone_LEDControl.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual | ~LEDControl (void) |
| Destructor. More... | |
| LEDControl (void) | |
| Constructor. More... | |
| virtual bool | is_valid (void) |
| Look for the BeagleBone LEDs and determine if they can be accessed and controled by this class. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | toggle (const SG::BeagleBone::LED led, const bool enabled) |
| Turn on or turn off the specified LED. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | turn_on (const SG::BeagleBone::LED led) |
| Turn on the specified LED. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | turn_off (const SG::BeagleBone::LED led) |
| Turn off the specified LED. More... | |
| virtual std::string | get_base_path (const SG::BeagleBone::LED led) |
| Determine the base path to access the given LED. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | set_trigger (const SG::BeagleBone::LED led, const SG::BeagleBone::Trigger trigger) |
| The trigger determines how a LED may be automatically enabled or disabled. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | set_default_trigger (const SG::BeagleBone::LED led) |
| Set the trigger back to the default value typically used when a BeagleBone first boots up. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | clear_idle_timeout (void) |
| Remove the idle timeout. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | update_activity_timestamp (void) |
| Update the activity timestamp so LEDControl knows the device has not gone idle. More... | |
| virtual LEDPattern | load_random_pattern (const size_t minimum_number_of_steps=2) |
| Load a random pattern. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | invert_pattern (void) |
| Invert the pattern in LEDControl (if any). More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | start_blink_thread (void) |
| Start the LED blink thread. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | stop_blink_thread (void) |
| Stop the LED blink thread. This can safely be called multiple times. More... | |
| virtual void | blink_loop (void) |
| Step through the blink pattern. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | set_idle_timeout (const size_t timeout_in_seconds=600, const LEDPattern pattern=LEDPattern::none) |
| After a certain amount of time when LEDControl isn't told to do something, it can consider this as the device having gone idle and apply a certain blink pattern. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | set_idle_timeout (const std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::duration timeout, const LEDPattern pattern=LEDPattern::none) |
| After a certain amount of time when LEDControl isn't told to do something, it can consider this as the device having gone idle and apply a certain blink pattern. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | set_idle_timeout (const std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::duration timeout, const SG::BeagleBone::BlinkPattern pattern) |
| After a certain amount of time when LEDControl isn't told to do something, it can consider this as the device having gone idle and apply a certain blink pattern. More... | |
| virtual bool | is_idle (const std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point &now) const |
| Determine if the device is idle. More... | |
| virtual bool | is_idle (void) const |
| Determine if the device is idle. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | load_pattern (const BlinkPattern &pattern) |
| Load the given blink pattern. More... | |
| virtual LEDControl & | load_pattern (const LEDPattern pattern) |
| Load the given blink pattern. More... | |
Public Attributes | |
| std::thread | blink_thread |
| Used to start a secondary thread to blink the lights in a given pattern. More... | |
| std::string | error_message |
| Store a short text message if LEDControl runs into a problem. More... | |
| std::atomic< bool > | blink_loop_should_continue |
| Fine-tune how blink_loop() behaves while it is running. More... | |
| std::atomic< size_t > | blink_interval_in_milliseconds |
| The amount of time to wait between each step in the blink pattern. Default value is 250 milliseconds. More... | |
| std::atomic< size_t > | blink_step_index |
| How far into the blink pattern we are. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| bool | valid |
| Determine if this BeagleBone LED control class has found the LEDs. More... | |
| std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point | last_activity |
| Last recorded activity. Used by blink_thread to determine if the device is idle. More... | |
| std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::duration | idle_timeout |
| The length of time that must elapse before the device is considered idle. More... | |
| std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point | idle_timepoint |
| Timestamp when the device is considered to have gone idle. More... | |
| BlinkPattern | idle_pattern |
| Pattern to use when the device goes idle. More... | |
| BlinkPattern | blink_pattern |
| The current blink pattern for the lights. More... | |
| std::string | led_base_path |
| The base path used to access the individual LEDs. More... | |
| std::vector< size_t > | vector_of_random_pattern_enum_values |
| Used by load_random_pattern() to keep track of which patterns haven't yet been shown. More... | |
| enum | ActionOnDestruction { ActionOnDestruction::invalid = 0, ActionOnDestruction::do_nothing, ActionOnDestruction::turn_on_all_leds, ActionOnDestruction::turn_off_all_leds, ActionOnDestruction::restore_default_triggers } |
| Determine what to do about the LEDs when the LEDControl object goes out of scope. More... | |
| ActionOnDestruction | action_on_destruction |
| Determine what to do about the LEDs when the LEDControl object goes out of scope. More... | |
BeagleBone LED software controller.
The BeagleBone LEDs are unrelated to Grove, but the SG++ library can be used to control some aspects of the LEDs. There are 4 LEDs on the top of both the BeagleBone Black (BBB) and the BeagleBone Green (BBG). The LEDs can be independently turned on, turned off, made to blink according to a pattern, or set to automatically turn on and off based on some hardware events.
Write access to the LEDs is typically only for the root user. If your application is not running as root, you'll want to ensure the trigger and brightness files have the right permissions and/or owner so they can be written to by SG++. For example:
The full path to these files depends on both the distribution and version of Linux in use on the BeagleBone. The method LEDControl::get_base_path() can be used to find the right files. Note there are 4 LEDs, and the SG++ library needs write access to both files per LED (trigger and brightness), so 8 files in all.
Typical use would be:
Another example where specific LEDs are turned on or off:
|
strong |
Determine what to do about the LEDs when the LEDControl object goes out of scope.
Normally, the default triggers are restored so there is some LED activity on the BeagleBone. But you can also decide to leave the LEDs as-is, turn them all on, or turn them all off.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| invalid | |
| do_nothing | |
| turn_on_all_leds | |
| turn_off_all_leds | |
| restore_default_triggers | |
|
virtual |
Destructor.
References action_on_destruction, SG::BeagleBone::all, blink_loop_should_continue, restore_default_triggers, set_default_trigger(), stop_blink_thread(), toggle(), turn_off_all_leds, turn_on_all_leds, and valid.
| SG::BeagleBone::LEDControl::LEDControl | ( | void | ) |
Constructor.
Example code:
The constructor:
References is_valid(), load_pattern(), and SG::BeagleBone::none.

|
virtual |
Step through the blink pattern.
This method will loop until stop_blink_thread() is called, or until blink_loop_should_continue is set to false. This method is normally started as a secondary thread by calling start_blink_thread().
References SG::BeagleBone::all, blink_interval_in_milliseconds, blink_loop_should_continue, blink_pattern, blink_step_index, idle_pattern, is_idle(), SG::BeagleBone::min, SG::BeagleBone::none, set_trigger(), toggle(), and valid.
Referenced by load_pattern(), and start_blink_thread().
|
inlinevirtual |
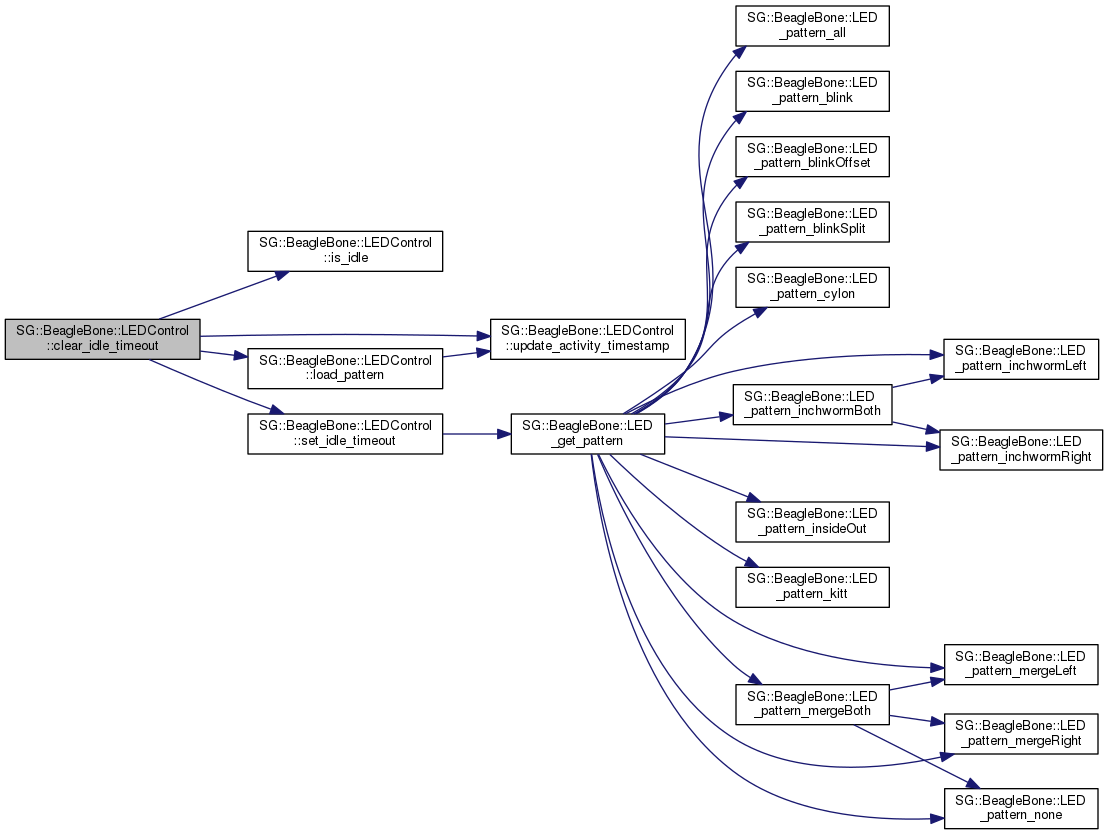
Remove the idle timeout.
This prevents LEDControl from ever going into the "idle timeout" state. This is the same as calling set_idle_timeout() with a timeout of zero seconds.
References is_idle(), load_pattern(), set_idle_timeout(), and update_activity_timestamp().
|
virtual |
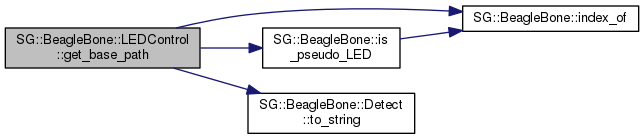
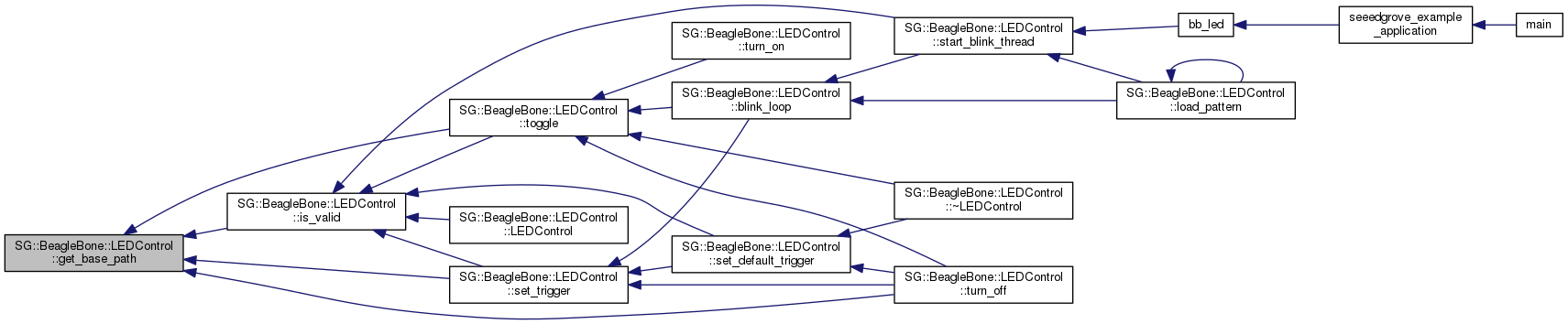
Determine the base path to access the given LED.
You normally wont need to call this, as it is used internally by the LEDControl class.
For example, this could return "/sys/devices/platform/leds/leds/beaglebone:green:usr2".
References SG::BeagleBone::index_of(), SG::BeagleBone::is_pseudo_LED(), led_base_path, and SG::BeagleBone::Detect::to_string().
Referenced by is_valid(), set_trigger(), toggle(), and turn_off().
|
virtual |
Invert the pattern in LEDControl (if any).
Example code:
References blink_pattern, SG::BeagleBone::LED_invert_pattern(), and load_pattern().
Referenced by load_pattern().

|
virtual |
Determine if the device is idle.
If set_idle_timeout() has not been called, then this method will return false. Otherwise, the return value depends on the timeout compared to when the method update_activity_timestamp() was last called.
References idle_timepoint.
|
virtual |
Determine if the device is idle.
If set_idle_timeout() has not been called, then this method will return false. Otherwise, the return value depends on the timeout compared to when the method update_activity_timestamp() was last called.
References idle_timepoint.
Referenced by blink_loop(), and clear_idle_timeout().
|
virtual |
Look for the BeagleBone LEDs and determine if they can be accessed and controled by this class.
If this returns false – indicating that the LEDs weren't properly detected – all other methods in this class will return without performing any action on the LEDs when called.
This method is automatically called by the constructor.
Depending on the distro or version of the linux software installed, look for the LEDs in one of several possible locations. From past experience, look for something like one of these:
"/sys/class/leds/beaglebone:green:usr0/brightness" "/sys/devices/leds/leds/beaglebone:green:usr0/brightness" "/sys/devices/platform/leds/leds/beaglebone:green:usr0/brightness" "/sys/devices/ocp.3/gpio-leds.8/leds/beaglebone:green:usr0/brightness" References error_message, get_base_path(), led_base_path, SG::BeagleBone::usr0, and valid.
Referenced by LEDControl(), set_default_trigger(), set_trigger(), start_blink_thread(), and toggle().


|
virtual |
Load the given blink pattern.
The default pattern set in LEDControl::LEDControl() is LEDPattern::none which turns off all LEDs, so you'll likely want to provide a different pattern to use if you want to see the LEDs blink.
If the blink loop is already running when load_pattern() is called, the new pattern will take effect within 100 milliseconds.
Example code:
References blink_pattern, blink_step_index, and update_activity_timestamp().
Referenced by clear_idle_timeout(), invert_pattern(), LEDControl(), and load_random_pattern().

|
inlinevirtual |
Load the given blink pattern.
The default pattern set in LEDControl::LEDControl() is LEDPattern::none which turns off all LEDs, so you'll likely want to provide a different pattern to use if you want to see the LEDs blink.
If the blink loop is already running when load_pattern() is called, the new pattern will take effect within 100 milliseconds.
Example code:
References blink_loop(), invert_pattern(), SG::BeagleBone::LED_get_pattern(), load_pattern(), load_random_pattern(), start_blink_thread(), and stop_blink_thread().
Referenced by load_pattern().


|
virtual |
Load a random pattern.
The pattern will be different than the one currently loaded (if any) and may have multiple steps. By requiring at least 2 steps in the pattern, this means extremely simple patterns like LEDPattern::none and LEDPattern::all will be skipped.
srand() somewhere in your application prior to calling load_random_pattern(), otherwise the order in which patterns are loaded wont be random.Example code:
References blink_pattern, SG::BeagleBone::LED_get_pattern(), load_pattern(), SG::BeagleBone::max, SG::BeagleBone::min, and vector_of_random_pattern_enum_values.
Referenced by bb_led(), and load_pattern().

|
virtual |
Set the trigger back to the default value typically used when a BeagleBone first boots up.
Example code:
| [in] | led | If led is set to LED::all, then all 4 LEDs will be reset back to their default values. |
References SG::BeagleBone::all, SG::BeagleBone::default_trigger(), SG::BeagleBone::is_pseudo_LED(), is_valid(), set_trigger(), SG::BeagleBone::usr0, SG::BeagleBone::usr1, SG::BeagleBone::usr2, and SG::BeagleBone::usr3.
Referenced by turn_off(), and ~LEDControl().

|
virtual |
After a certain amount of time when LEDControl isn't told to do something, it can consider this as the device having gone idle and apply a certain blink pattern.
This will only happen if both set_idle_timeout() and start_blink_thread() have been called, since the blink thread is what checks for idleness and takes care of toggling the lights.
For example, the LEDs can be set to blink after 5 minutes of idleness:
References SG::BeagleBone::LED_get_pattern().
Referenced by clear_idle_timeout(), set_idle_timeout(), and turn_off().

|
virtual |
After a certain amount of time when LEDControl isn't told to do something, it can consider this as the device having gone idle and apply a certain blink pattern.
This will only happen if both set_idle_timeout() and start_blink_thread() have been called, since the blink thread is what checks for idleness and takes care of toggling the lights.
For example, the LEDs can be set to blink after 5 minutes of idleness:
References SG::BeagleBone::LED_get_pattern(), and set_idle_timeout().
|
virtual |
After a certain amount of time when LEDControl isn't told to do something, it can consider this as the device having gone idle and apply a certain blink pattern.
This will only happen if both set_idle_timeout() and start_blink_thread() have been called, since the blink thread is what checks for idleness and takes care of toggling the lights.
For example, the LEDs can be set to blink after 5 minutes of idleness:
References idle_pattern, idle_timeout, idle_timepoint, and update_activity_timestamp().

|
virtual |
The trigger determines how a LED may be automatically enabled or disabled.
This method sets each individual trigger file to a specific value. For example, the name of a trigger file could be "/sys/devices/platform/leds/leds/beaglebone:green:usr3/trigger". By default, the 4 LEDs have triggers such as heartbeat and mmc0 to indicate different activies on the BeagleBone.
If you want to manually toggle some LEDs on and off, the trigger must first be set to none. Otherwise, your on or off values will get overwritten by the normal activity, such as the heartbeat or CPU activity.
Trigger::none for all 4 LEDs in blink_loop(), so you'll only need to call set_trigger() if you want to do something with the LEDs other than the usual pattern and blink loop thread.Example code:
| [in] | led | If led is set to LED::all, then the trigger for all 4 LEDs will be set. |
| [in] | trigger | Value to use for the trigger. To prevent the LEDs from automatically changing, use Trigger::none. |
trigger file cannot be written. (Verify file or user permissions?)References SG::BeagleBone::all, error_message, get_base_path(), SG::BeagleBone::is_pseudo_LED(), is_valid(), SG::BeagleBone::to_string(), update_activity_timestamp(), SG::BeagleBone::usr0, SG::BeagleBone::usr1, SG::BeagleBone::usr2, and SG::BeagleBone::usr3.
Referenced by blink_loop(), set_default_trigger(), and turn_off().
|
virtual |
Start the LED blink thread.
This can safely be called multiple times. It doesn't matter if this is called before or after load_pattern().
Example code:
References blink_loop(), blink_loop_should_continue, blink_thread, is_valid(), and update_activity_timestamp().
Referenced by bb_led(), and load_pattern().

|
virtual |
Stop the LED blink thread. This can safely be called multiple times.
This method doesn't return until the blink thread has stopped.
References blink_loop_should_continue, blink_thread, and update_activity_timestamp().
Referenced by load_pattern(), and ~LEDControl().
|
virtual |
Turn on or turn off the specified LED.
Example code:
| [in] | led | If led is set to LED::all, then all 4 LEDs will be toggled together. |
| [in] | enabled | Set enabled to true to turn on a LED, or set to false to turn it off. |
brightness file cannot be written. (Verify file or user permissions?)References SG::BeagleBone::all, error_message, get_base_path(), SG::BeagleBone::is_pseudo_LED(), is_valid(), SG::BeagleBone::usr0, SG::BeagleBone::usr1, SG::BeagleBone::usr2, and SG::BeagleBone::usr3.
Referenced by blink_loop(), turn_off(), turn_on(), and ~LEDControl().
|
inlinevirtual |
Turn off the specified LED.
This is an alias for LEDControl::toggle(..., false).
Example code:
References get_base_path(), SG::BeagleBone::none, set_default_trigger(), set_idle_timeout(), set_trigger(), and toggle().
|
inlinevirtual |
Turn on the specified LED.
This is an alias for LEDControl::toggle(..., true).
Example code:
References toggle().

|
virtual |
Update the activity timestamp so LEDControl knows the device has not gone idle.
Several LEDControl methods call this internally to indicate the LEDControl object isn't idle. Applications can also regularly call this to prevent LEDControl from going into an idle state. Otherwise, once the time described in set_idle_timeout() has elapsed, the device will be considered "idle".
References idle_timeout, idle_timepoint, and last_activity.
Referenced by clear_idle_timeout(), load_pattern(), set_idle_timeout(), set_trigger(), start_blink_thread(), and stop_blink_thread().
| ActionOnDestruction SG::BeagleBone::LEDControl::action_on_destruction |
Determine what to do about the LEDs when the LEDControl object goes out of scope.
Normally, the default triggers are restored so there is some LED activity on the BeagleBone. But you can also decide to leave the LEDs as-is, turn them all on, or turn them all off.
Referenced by ~LEDControl().
| std::atomic<size_t> SG::BeagleBone::LEDControl::blink_interval_in_milliseconds |
The amount of time to wait between each step in the blink pattern. Default value is 250 milliseconds.
Referenced by blink_loop().
| std::atomic<bool> SG::BeagleBone::LEDControl::blink_loop_should_continue |
Fine-tune how blink_loop() behaves while it is running.
Set this to false to force the blink loop to immediately exit.
Referenced by blink_loop(), start_blink_thread(), stop_blink_thread(), and ~LEDControl().
|
protected |
The current blink pattern for the lights.
Referenced by blink_loop(), invert_pattern(), load_pattern(), and load_random_pattern().
| std::atomic<size_t> SG::BeagleBone::LEDControl::blink_step_index |
How far into the blink pattern we are.
This resets back to zero once the end of a pattern is reached.
Referenced by blink_loop(), and load_pattern().
| std::thread SG::BeagleBone::LEDControl::blink_thread |
Used to start a secondary thread to blink the lights in a given pattern.
Referenced by start_blink_thread(), and stop_blink_thread().
| std::string SG::BeagleBone::LEDControl::error_message |
Store a short text message if LEDControl runs into a problem.
Referenced by is_valid(), set_trigger(), and toggle().
|
protected |
Pattern to use when the device goes idle.
Referenced by blink_loop(), and set_idle_timeout().
|
protected |
The length of time that must elapse before the device is considered idle.
Referenced by set_idle_timeout(), and update_activity_timestamp().
|
protected |
Timestamp when the device is considered to have gone idle.
Referenced by is_idle(), set_idle_timeout(), and update_activity_timestamp().
|
protected |
Last recorded activity. Used by blink_thread to determine if the device is idle.
Referenced by update_activity_timestamp().
|
protected |
The base path used to access the individual LEDs.
Referenced by get_base_path(), and is_valid().
|
protected |
Determine if this BeagleBone LED control class has found the LEDs.
If this is false, then it means the BeagleBone LEDs were not detected, or cannot be accessed.
Referenced by blink_loop(), is_valid(), and ~LEDControl().
|
protected |
Used by load_random_pattern() to keep track of which patterns haven't yet been shown.
Referenced by load_random_pattern().