A dense matrix of values of type T.
More...
#include <matrix.hpp>

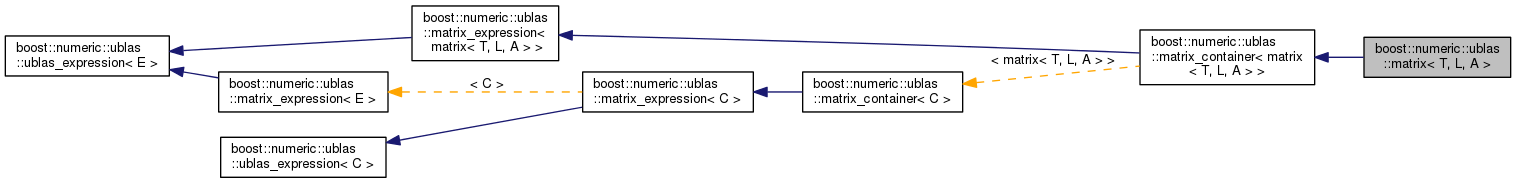
Classes | |
| class | const_iterator1 |
| class | const_iterator2 |
| class | iterator1 |
| class | iterator2 |
Public Types | |
| typedef A::size_type | size_type |
| typedef A::difference_type | difference_type |
| typedef T | value_type |
| typedef const T & | const_reference |
| typedef T & | reference |
| typedef A | array_type |
| typedef const matrix_reference < const self_type > | const_closure_type |
| typedef matrix_reference < self_type > | closure_type |
| typedef vector< T, A > | vector_temporary_type |
| typedef self_type | matrix_temporary_type |
| typedef dense_tag | storage_category |
| typedef L::orientation_category | orientation_category |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base1 < const_iterator1 > | const_reverse_iterator1 |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base1 < iterator1 > | reverse_iterator1 |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base2 < const_iterator2 > | const_reverse_iterator2 |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base2 < iterator2 > | reverse_iterator2 |
| typedef matrix< T, L, A > | container_type |
| typedef matrix_tag | type_category |
| typedef E | expression_type |
Public Member Functions | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE | matrix () |
| Default dense matrix constructor. Make a dense matrix of size (0,0) More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE | matrix (size_type size1, size_type size2) |
| Dense matrix constructor with defined size. More... | |
| matrix (size_type size1, size_type size2, const value_type &init) | |
| Dense matrix constructor with defined size a initial value for all the matrix elements. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE | matrix (size_type size1, size_type size2, const array_type &data) |
| Dense matrix constructor with defined size and an initial data array. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE | matrix (const matrix &m) |
| Copy-constructor of a dense matrix. More... | |
| template<class AE > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE | matrix (const matrix_expression< AE > &ae) |
| Copy-constructor of a dense matrix from a matrix expression. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE size_type | size1 () const |
| Return the number of rows of the matrix You can also use the free size<>() function in operation/size.hpp as size<1>(m) where m is a matrix. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE size_type | size2 () const |
| Return the number of colums of the matrix You can also use the free size<>() function in operation/size.hpp as size<2>(m) where m is a matrix. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const array_type & | data () const |
| Return a constant reference to the internal storage of a dense matrix, i.e. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE array_type & | data () |
| Return a reference to the internal storage of a dense matrix, i.e. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE void | resize (size_type size1, size_type size2, bool preserve=true) |
| Resize a matrix to new dimensions If data are preserved, then if the size if bigger at least on one dimension, extra values are filled with zeros. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reference | operator() (size_type i, size_type j) const |
| Access a matrix element. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE reference | at_element (size_type i, size_type j) |
| Access a matrix element. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE reference | operator() (size_type i, size_type j) |
| Access a matrix element. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE reference | insert_element (size_type i, size_type j, const_reference t) |
| Change the value of a matrix element. More... | |
| void | erase_element (size_type i, size_type j) |
| Erase the element For most types (int, double, etc...) it means setting 0 (zero) the element at zero in fact. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE void | clear () |
| Erase all elements in the matrix For most types (int, double, etc...) it means writing 0 (zero) everywhere. More... | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator= (const matrix &m) |
| template<class C > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator= (const matrix_container< C > &m) |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | assign_temporary (matrix &m) |
| template<class AE > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator= (const matrix_expression< AE > &ae) |
| template<class AE > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | assign (const matrix_expression< AE > &ae) |
| template<class AE > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator+= (const matrix_expression< AE > &ae) |
| template<class C > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator+= (const matrix_container< C > &m) |
| template<class AE > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | plus_assign (const matrix_expression< AE > &ae) |
| template<class AE > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator-= (const matrix_expression< AE > &ae) |
| template<class C > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator-= (const matrix_container< C > &m) |
| template<class AE > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | minus_assign (const matrix_expression< AE > &ae) |
| template<class AT > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator*= (const AT &at) |
| template<class AT > | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE matrix & | operator/= (const AT &at) |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE void | swap (matrix &m) |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator1 | find1 (int, size_type i, size_type j) const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE iterator1 | find1 (int, size_type i, size_type j) |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator2 | find2 (int, size_type i, size_type j) const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE iterator2 | find2 (int, size_type i, size_type j) |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator1 | begin1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator1 | cbegin1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator1 | end1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator1 | cend1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE iterator1 | begin1 () |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE iterator1 | end1 () |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator2 | begin2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator2 | cbegin2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator2 | end2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_iterator2 | cend2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE iterator2 | begin2 () |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE iterator2 | end2 () |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator1 | rbegin1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator1 | crbegin1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator1 | rend1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator1 | crend1 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE reverse_iterator1 | rbegin1 () |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE reverse_iterator1 | rend1 () |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator2 | rbegin2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator2 | crbegin2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator2 | rend2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const_reverse_iterator2 | crend2 () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE reverse_iterator2 | rbegin2 () |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE reverse_iterator2 | rend2 () |
| template<class Archive > | |
| void | serialize (Archive &ar, const unsigned int) |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE const container_type & | operator() () const |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE container_type & | operator() () |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static const unsigned | complexity |
Friends | |
| BOOST_UBLAS_INLINE friend void | swap (matrix &m1, matrix &m2) |
A dense matrix of values of type T.
For a 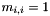 -dimensional matrix and
-dimensional matrix and 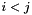 , every element
, every element 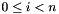 is mapped to the
is mapped to the 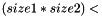 -th element of the container for row major orientation or the
-th element of the container for row major orientation or the 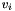 -th element of the container for column major orientation. In a dense matrix all elements are represented in memory in a contiguous chunk of memory by definition.
-th element of the container for column major orientation. In a dense matrix all elements are represented in memory in a contiguous chunk of memory by definition.
Orientation and storage can also be specified, otherwise a row_major and unbounded_array are used. It is not required by the storage to initialize elements of the matrix.
| T | the type of object stored in the matrix (like double, float, complex, etc...) |
| L | the storage organization. It can be either row_major or column_major. Default is row_major |
| A | the type of Storage array. Default is unbounded_array |
| typedef A boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::array_type |
| typedef matrix_reference<self_type> boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::closure_type |
| typedef const matrix_reference<const self_type> boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_closure_type |
| typedef const T& boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_reference |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base1<const_iterator1> boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_reverse_iterator1 |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base2<const_iterator2> boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_reverse_iterator2 |
|
inherited |
| typedef A::difference_type boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::difference_type |
|
inherited |
| typedef self_type boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::matrix_temporary_type |
| typedef L::orientation_category boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::orientation_category |
| typedef T& boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::reference |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base1<iterator1> boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::reverse_iterator1 |
| typedef reverse_iterator_base2<iterator2> boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::reverse_iterator2 |
| typedef A::size_type boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::size_type |
| typedef dense_tag boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::storage_category |
|
inherited |
| typedef T boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::value_type |
| typedef vector<T, A> boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::vector_temporary_type |
|
inline |
Default dense matrix constructor. Make a dense matrix of size (0,0)
|
inline |
Dense matrix constructor with defined size.
| size1 | number of rows |
| size2 | number of columns |
|
inline |
Dense matrix constructor with defined size a initial value for all the matrix elements.
| size1 | number of rows |
| size2 | number of columns |
| init | initial value assigned to all elements |
|
inline |
Dense matrix constructor with defined size and an initial data array.
| size1 | number of rows |
| size2 | number of columns |
| data | array to copy into the matrix. Must have the same dimension as the matrix |
|
inline |
Copy-constructor of a dense matrix.
| m | is a dense matrix |
|
inline |
Copy-constructor of a dense matrix from a matrix expression.
| ae | is a matrix expression |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Access a matrix element.
Here we return a reference
| i | the first coordinate of the element. By default it's the row |
| j | the second coordinate of the element. By default it's the column |
Referenced by boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::erase_element(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::insert_element(), and boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::operator()().
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Erase all elements in the matrix For most types (int, double, etc...) it means writing 0 (zero) everywhere.
For user-defined types, it could be another value if you decided it. Your type in that case must contain a default null value.
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Return a constant reference to the internal storage of a dense matrix, i.e.
the raw data It's type depends on the type used by the matrix to store its data
Referenced by boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::at_element(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::clear(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::find1(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::find2(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::operator()(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::operator=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::resize(), and boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::swap().
|
inline |
Return a reference to the internal storage of a dense matrix, i.e.
the raw data It's type depends on the type used by the matrix to store its data
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Erase the element For most types (int, double, etc...) it means setting 0 (zero) the element at zero in fact.
For user-defined types, it could be another value if you decided it. Your type in that case must contain a default null value.
| i | the first coordinate of the element. By default it's the row |
| j | the second coordinate of the element. By default it's the column |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Change the value of a matrix element.
Return back a reference to it
| i | the first coordinate of the element. By default it's the row |
| j | the second coordinate of the element. By default it's the column |
| t | the new value of the element |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Access a matrix element.
Here we return a const reference
| i | the first coordinate of the element. By default it's the row |
| j | the second coordinate of the element. By default it's the column |
|
inline |
Access a matrix element.
Here we return a reference
| i | the first coordinate of the element. By default it's the row |
| j | the second coordinate of the element. By default it's the column |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inlineinherited |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
|
inline |
Resize a matrix to new dimensions If data are preserved, then if the size if bigger at least on one dimension, extra values are filled with zeros.
If data are not preserved, then nothing has to be assumed regarding the content of the matrix after resizing.
| size1 | the new number of rows |
| size2 | the new number of colums |
| preserve | a boolean to say if one wants the data to be preserved during the resizing. Default is true. |
Referenced by boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::operator=(), boost::numeric::odeint::resize_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T2, L2, A2 > >::resize(), and boost::numeric::odeint::resize_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::vector< T_V, A_V > >::resize().
|
inline |
|
inline |
Return the number of rows of the matrix You can also use the free size<>() function in operation/size.hpp as size<1>(m) where m is a matrix.
Referenced by boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::operator=(), boost::numeric::odeint::resize_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T2, L2, A2 > >::resize(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::resize(), boost::numeric::odeint::same_size_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T2, L2, A2 > >::same_size(), and boost::numeric::odeint::same_size_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::vector< T_V, A_V > >::same_size().
|
inline |
Return the number of colums of the matrix You can also use the free size<>() function in operation/size.hpp as size<2>(m) where m is a matrix.
Referenced by boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator*(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator++(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator+=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator-(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator-(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator-(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator-(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator--(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator1::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator1::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::const_iterator2::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >::iterator2::operator-=(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::operator=(), boost::numeric::odeint::resize_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T2, L2, A2 > >::resize(), boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, bounded_array< T, M *N > >::resize(), boost::numeric::odeint::same_size_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T2, L2, A2 > >::same_size(), and boost::numeric::odeint::same_size_impl< boost::numeric::ublas::matrix< T, L, A >, boost::numeric::ublas::vector< T_V, A_V > >::same_size().
|
inline |
|
friend |
|
staticinherited |